What Are Auto Stamping Parts and Why They Are Essential to the Automotive Industry
In the ever-evolving automotive sector, few manufacturing processes are as vital and widespread as metal stamping. The components produced through this technology, commonly referred to as auto stamping parts, are the hidden backbone of modern vehicles. As the industry transitions toward lightweighting, electrification, and higher safety standards, stamping remains one of the most efficient and reliable ways to produce high-quality automotive components.
What Are Auto Stamping Parts?
Auto stamping parts are metal components formed by applying pressure to flat sheet metal using stamping dies and powerful presses. By combining techniques such as punching, bending, stretching, and flanging, stamping transforms raw sheets of steel, aluminum, or advanced alloys into precise automotive components.
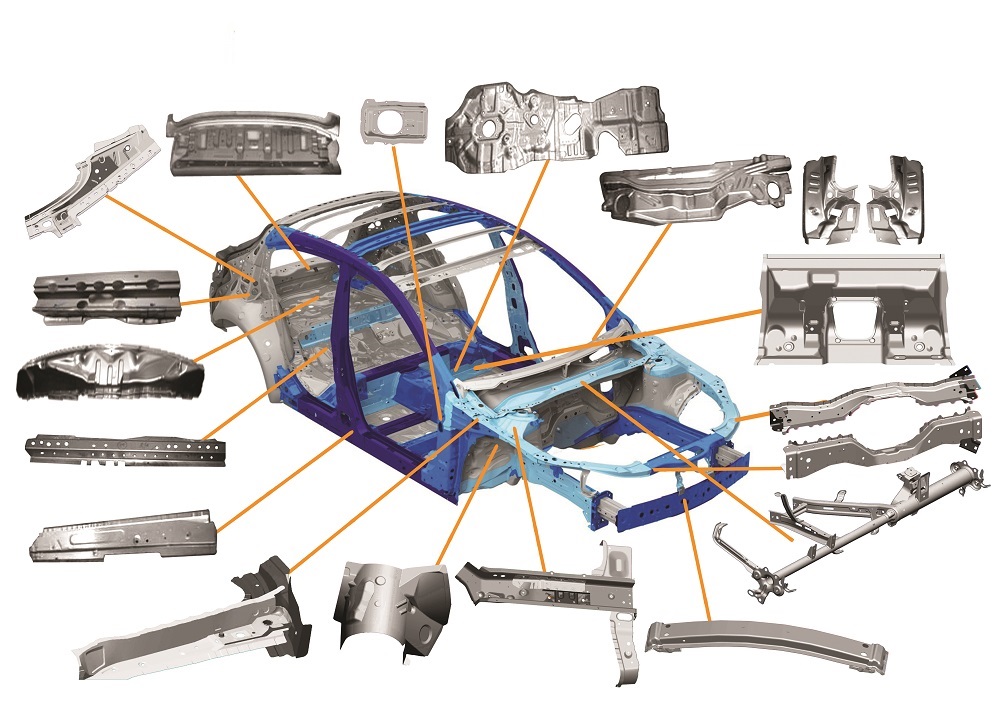
These parts cover a wide spectrum: from large exterior panels like hoods, doors, and fenders, to structural components such as chassis reinforcements, brackets, and mounts, and even small precision parts like clips and connectors. Regardless of size or function, each stamped part must meet strict industry requirements for strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy.
How Auto Stamping Works
The stamping process begins with material selection, usually steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or high-strength alloys, depending on the performance target. Sheets are then fed into stamping presses, which can apply forces of hundreds or even thousands of tons to shape the metal. Progressive or transfer dies are often used to achieve multiple operations—cutting, bending, and forming—within a single production cycle.
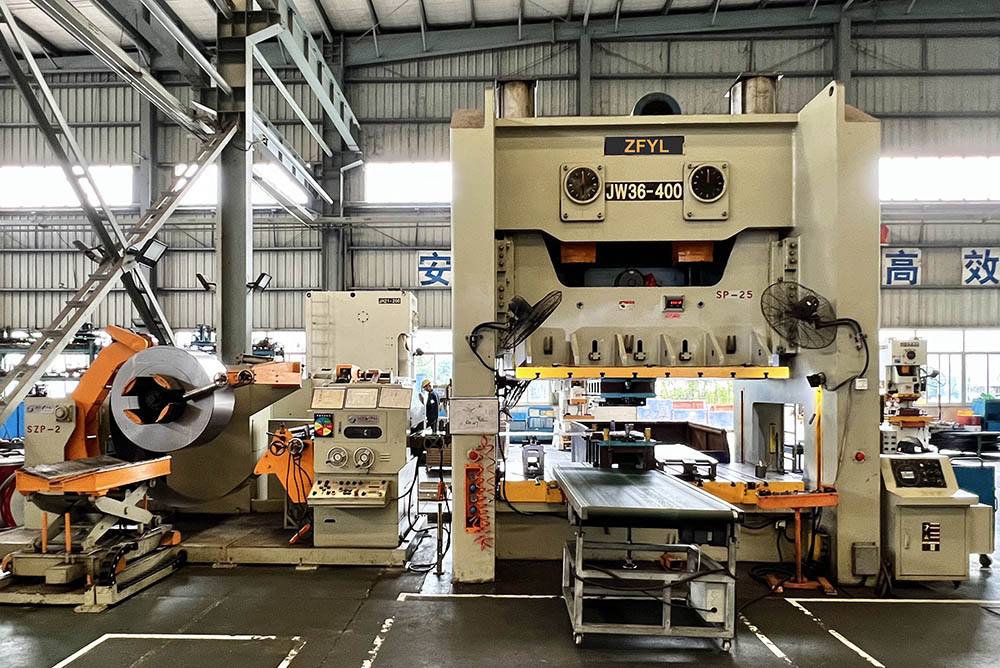

After stamping, many parts undergo surface treatments such as galvanizing, painting, or coating to improve corrosion resistance and extend service life. Advanced quality-control tools, including 3D scanning and automated inspection systems, ensure that every component conforms to strict automotive standards.
Benefits of Automotive Stamping
The popularity of stamping in the automotive industry comes from several clear advantages:
Mass Production Efficiency – Capable of producing thousands of identical parts per day.
High Precision – Tight tolerances ensure dimensional consistency.
Cost-Effectiveness – While tooling requires investment, per-unit costs are low in high volumes.
Versatility – Applicable to both structural and decorative parts across the vehicle.
Challenges and Industry Trends
Stamping is not without its challenges. Tooling design and maintenance can be costly, and high-strength steels or lightweight alloys place additional stress on equipment. However, the industry is rapidly adopting robotic automation, digital simulation, and smart factory solutions to improve efficiency and extend tool life.
Another major trend is lightweighting. With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), automakers are demanding more aluminum and advanced alloys for stamped parts, aiming to reduce weight while maintaining crash safety. This shift is reshaping stamping operations worldwide.
Applications Across the Vehicle
Stamped components are found in nearly every area of a car:
Body-in-White structures: roofs, side frames, floor panels.
Exterior panels: doors, hoods, trunk lids, fenders.
Chassis and suspension: brackets, reinforcements, mounts.
Interior and functional parts: seat frames, pedal brackets, clips.
EV-related parts: battery housings, motor enclosures, lightweight support structures.
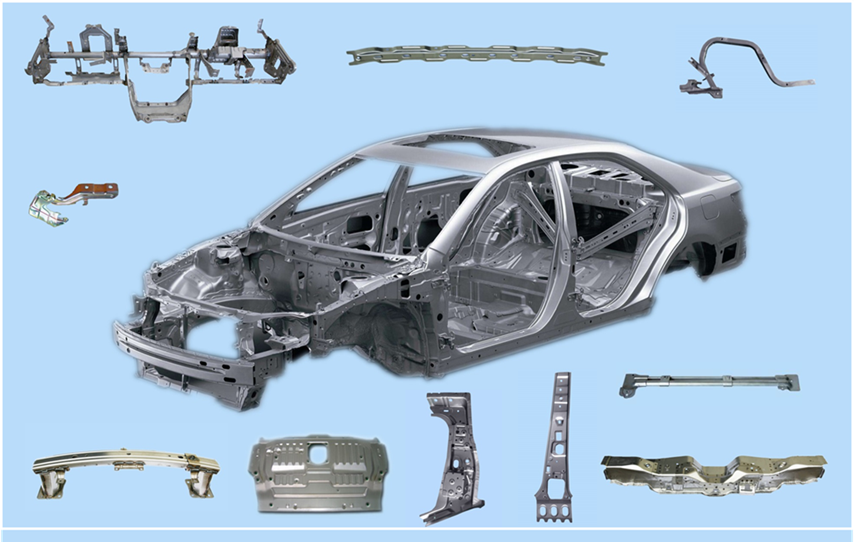
Outlook for the Future
Industry analysts predict steady growth in the global automotive stamping market, driven by the twin forces of vehicle electrification and sustainability goals. Investments in high-speed stamping presses, advanced materials, and eco-friendly surface treatments are expected to define the next generation of auto stamping parts.
As a result, suppliers capable of combining volume production with innovation will remain indispensable to automakers. Stamping will continue to evolve, but its role as the foundation of modern car manufacturing is set to endure.
Conclusion
Auto stamping parts may not be visible to consumers, yet they are indispensable to vehicle design, safety, and performance. As the industry embraces electrification and lightweighting, stamping technology will remain a cornerstone of production—quietly shaping the cars of the future.

